With the announcement that Google will begin including the “Core Web Vitals” (CWV) metrics in its search engine algorithm starting next year, many are scrambling to make sense of what exactly these metrics measure and how they work.
Unlike metrics such as “loading speed” or “dwell time” which are direct and simple to understand, Core Web Vitals combine a number of factors which can get very technical.
To help you prepare for the introduction of Core Web Vitals as a ranking signal next year, Google is sharing a comprehensive guide to what CWV measures, and how they can affect your website.
What Are Core Web Vitals
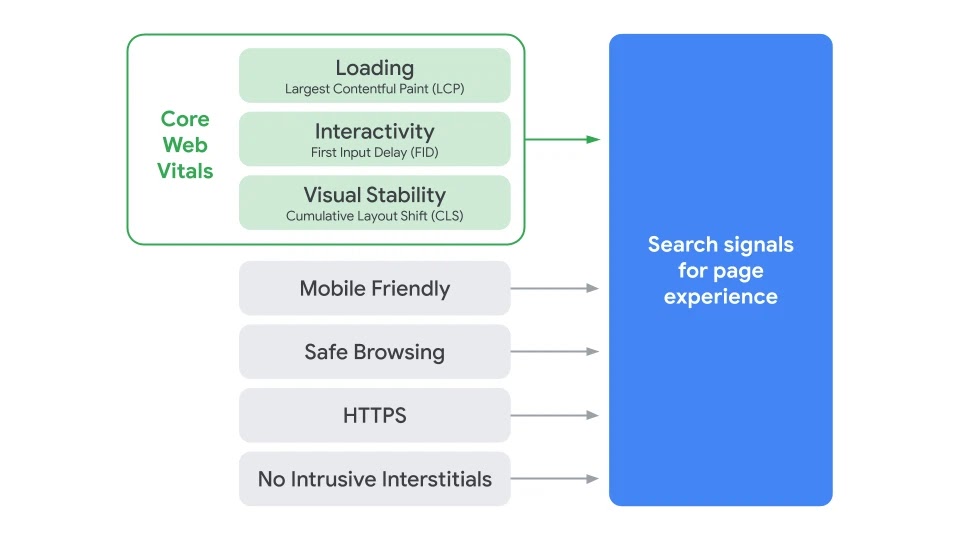
The first thing to understand is what exactly Core Web Vitals are. Simply put, CWV are a combination of three specific metrics assessing your page’s loading speed, usability, and stability. These three metrics appear very technical at first, but the gist is that your site needs to load quickly and provide a secure and easy to use experience. As for the specifics, Core Web Vitals include:
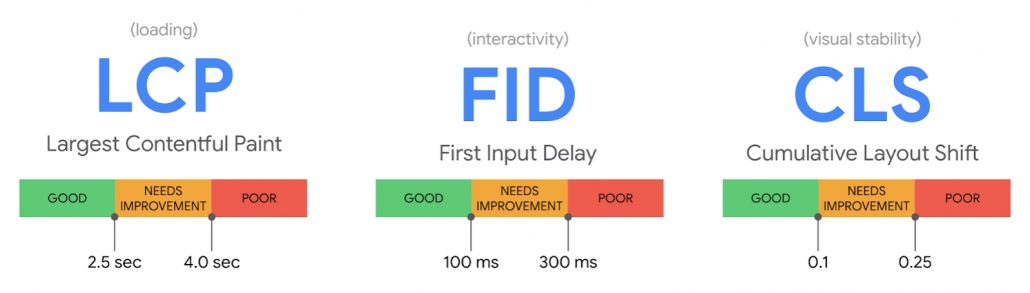
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to have LCP occur within the first 2.5 seconds of the page starting to load.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to have an FID of less than 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to have a CLS score of less than 0.1.
Importantly, in the new guide, Google reaffirmed its intention to start using Core Web Vitals as a ranking signal in 2021.
“Starting May 2021, Core Web vitals will be included in page experience signals together with existing search signals including mobile-friendliness, safe-browsing, HTTPS-security, and intrusive interstitial guidelines.”
Does Every Page Need To Meet CWV Standards?
In the help document, Google explains that the Core Web Vitals standards it set out should be seen as a mark to aim for, but not necessarily a requirement for good ranking.
Q: Is Google recommending that all my pages hit these thresholds? What’s the benefit?
A: We recommend that websites use these three thresholds as a guidepost for optimal user experience across all pages. Core Web Vitals thresholds are assessed at the per-page level, and you might find that some pages are above and others below these thresholds. The immediate benefit will be a better experience for users that visit your site, but in the long-term we believe that working towards a shared set of user experience metrics and thresholds across all websites, will be critical in order to sustain a healthy web ecosystem.
Will Core Web Vitals Make or Break Your Site?
It is unclear exactly how strongly Core Web Vitals metrics will be able to affect your site when they are implemented, but Google’s current stance suggests they will be a significant part of your ranking.
Q: How does Google determine which pages are affected by the assessment of Page Experience and usage as a ranking signal?
A: Page experience is just one of many signals that are used to rank pages. Keep in mind that intent of the search query is still a very strong signal, so a page with a subpar page experience may still rank highly if it has great, relevant content.
Other Details
Among the Q&A, Google also gives a few important details on the scope and impact of Core Web Vitals.
Q: Is there a difference between desktop and mobile ranking?
A: At this time, using page experience as a signal for ranking will apply only to mobile Search.
Q: What can site owners expect to happen to their traffic if they don’t hit Core Web Vitals performance metrics?
A: It’s difficult to make any kind of general prediction. We may have more to share in the future when we formally announce the changes are coming into effect. Keep in mind that the content itself and its match to the kind of information a user is seeking remains a very strong signal as well.
The full document covers a wide range of technical issues which will be relevant for any web designer or site manager, but the big picture remains the same. Google has been prioritizing sites with the best user experience for years, and the introduction of Core Web Vitals only advances that effort.