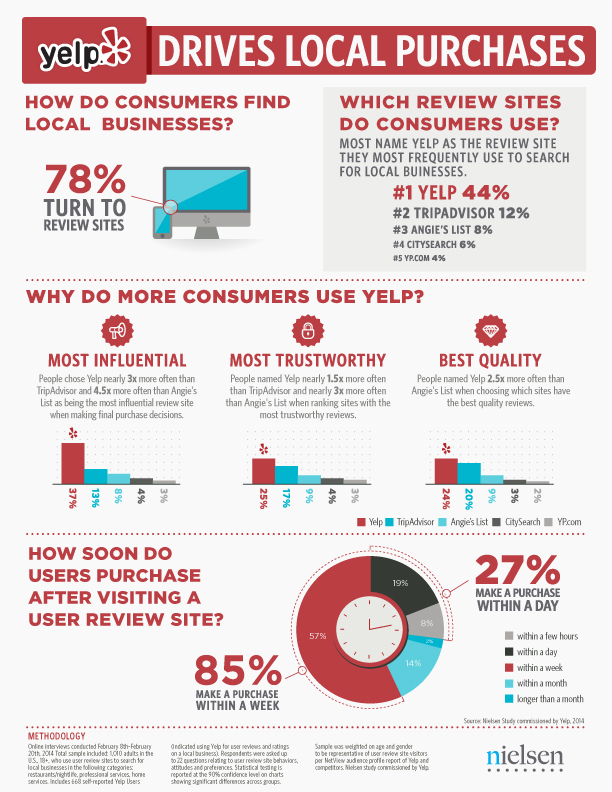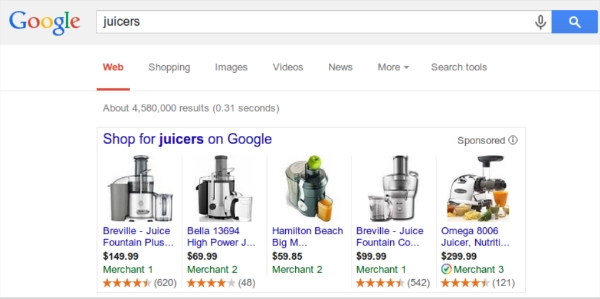
Google has been working hard to expand their reviews and ratings systems, and yesterday they made a big step by announcing that they will be introducing product ratings for Product Listing Ads (PLAs).
The announcement, which appeared on the Inside Adwords Blog, stated:
Product reviews provide critical information to shoppers making purchase decisions. To help shoppers easily find this information when searching for products, we’re introducing product ratings on Product Listing Ads.
Shoppers browsing on Google will see the typical product listings they have become accustomed to, but beneath the listings product ratings will also be shown in the shape of stars and review counts. For now it appears the changes will only be seen on search results within the United States.
The data used for these review listings will be gathered from multiple sources, such as merchants, third party aggregators, and editorial sites.
If reviews for businesses are any indication of what this change will bring, it seems very likely that businesses offering products with largely positive reviews will be able to leverage the updated listings to not only increase their click-through rates, but to also increase conversions overall.

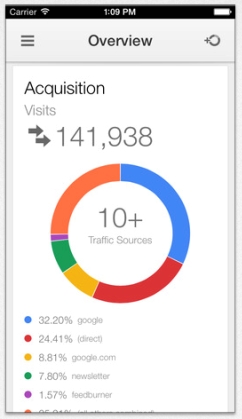 A few weeks ago
A few weeks ago The majority of reports about Facebook this year would suggest the largest social media platform is about to crumble under its own weight. But, all the latest data from their
The majority of reports about Facebook this year would suggest the largest social media platform is about to crumble under its own weight. But, all the latest data from their 
 That may not be the case for long, as Google has stepped up their fight against the technology.
That may not be the case for long, as Google has stepped up their fight against the technology.