The bad news is half or more of your website traffic likely comes from bots. The good news is that is actually a huge improvement from in the past.
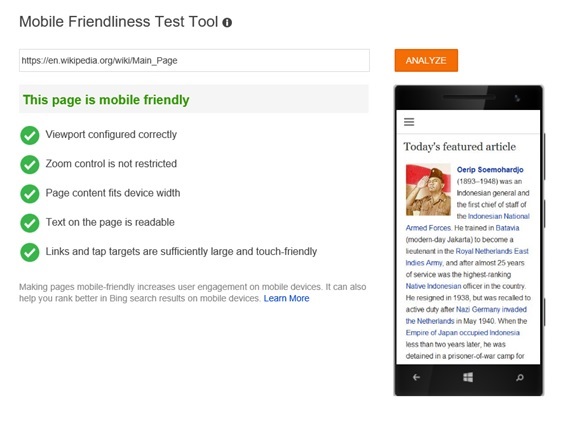
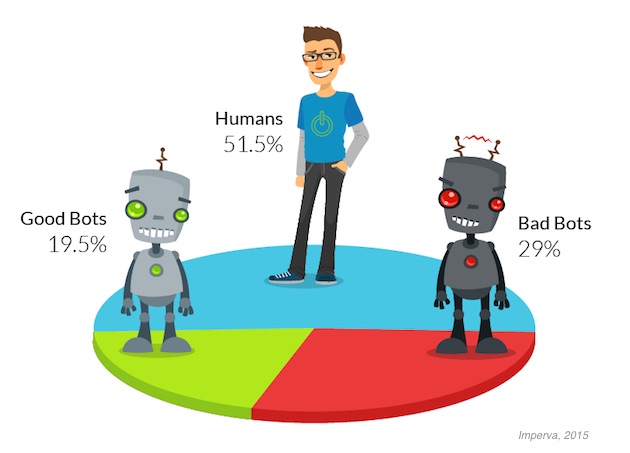
A new report from Imperva Incapsula shows that approximately 48.5% of all traffic to websites comes from bots, not actual online users. That number comes from a review of over 19 billion visits to 35,000 Incapsula client websites around the world with a minimum daily traffic count of at least 10 human visitors gathered over a 90 day period in 2015.
According to the data, 51.5% of all Web traffic comes from human users, while 29% come from “bad bots” which automate spam or other malicious activity, and 19.5% came from “good bots” which are used by search engines and other online services.
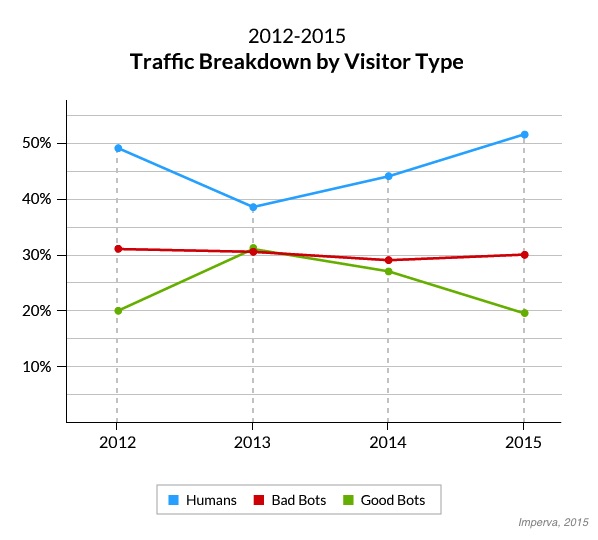
While this sounds bad, the share of human traffic is actually rising compared to past year. The report explains:
In a similar 2013 study conducted by Imperva, humans made up only 31.5% of all visits to sites, compared with 51.5% in 2015. This shift is mainly due to an increase in human traffic as more people use the Web and a decrease in good bot traffic.
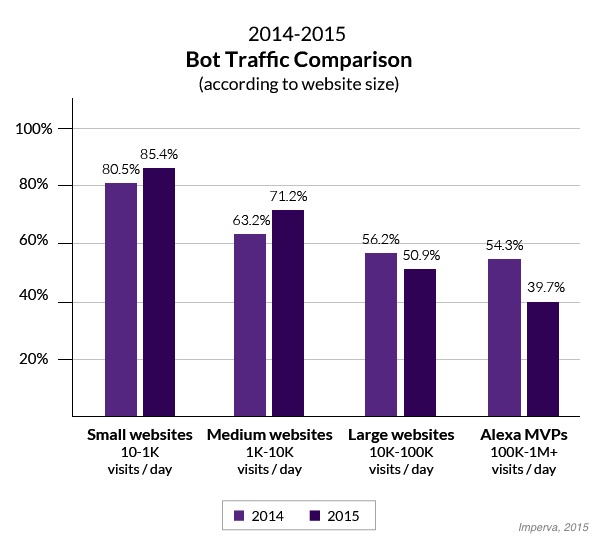
The ratio of bots-to-humans your website receives is likely influenced by how popular your site is, as the most popular sites examined showed the smallest ratio of bot traffic (39.7%). In comparison, the least popular sites included in the traffic had the highest share of bot traffic (85.4%).
No matter what percentage of your traffic comes to bots, the best solution is to continue emphasizing marketing that directly connects with real humans such as social media marketing and PPC.