TikTok is making it easier for brands of any size to use licensed music on the platform with its new Sounds for Businesses service.
With this, small businesses will be much more able to afford popular songs in their ads, videos, and other organic content through the TikTok Audio Library.
Why Licensed Music Is Important For Marketing
For brands trying to rise above the noise on social media, using licensed songs is a crucial part of getting users’ attention.
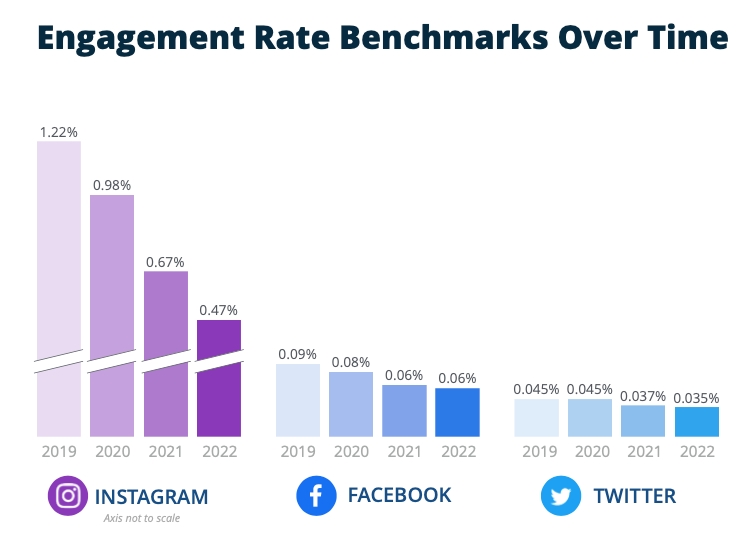
Even more, TikTok says its research shows 68% of users find remembering a brand’s message easier when it is paired with a popular song they like. Of those, 62% said they would take time to learn more about a brand if they enjoy the song. This is because users feel like a brand may have similar tastes to theirs if they choose music they like as well.
Unfortunately, licensing music is not easy – especially for smaller brands. It is not always clear who to contact to license a piece of music and costs can quickly stack up.
Trying to slip a popular song into your marketing materials without paying isn’t likely to work either. TikTok (and all other social networks) use automated tools to identify music that may be infringing on a copyright claim. When this happens, the app removes your audio entirely – potentially ruining your message in the process.
With this new library of licensed music, brands can now avoid this entire complicated and expensive process by choosing from over 500,000 licensed tunes and sounds.
How To Use TikTok Sounds for Businesses
TikTok’s Sounds for Businesses library is available to brands creating content and ads on both desktop and mobile.
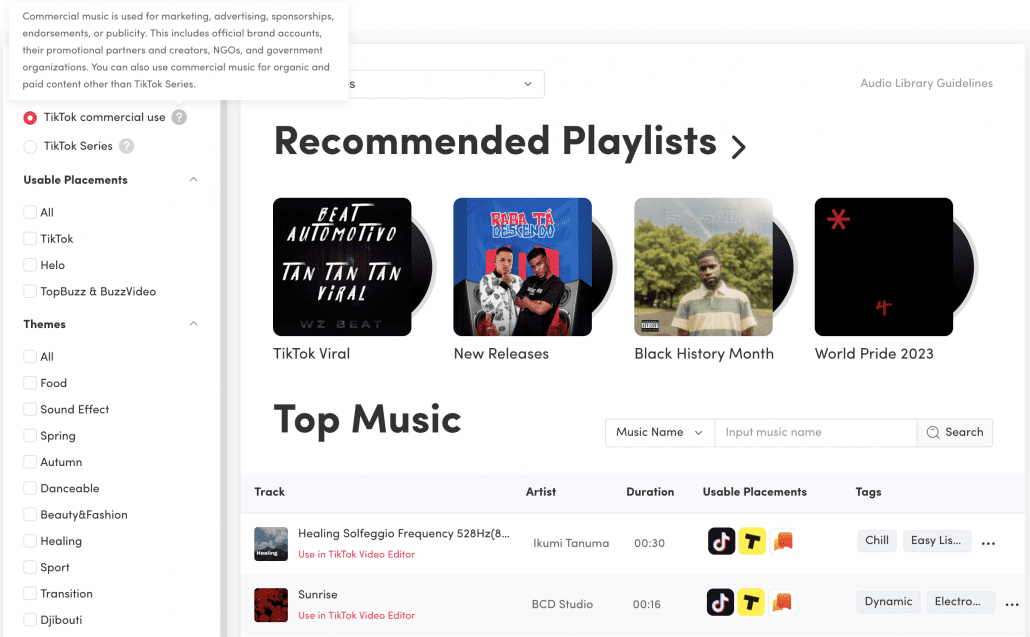
On desktop, the Audio Library is within the Creative Center. Here, you can filter audio by theme, genre, mood, and length to find the perfect match.
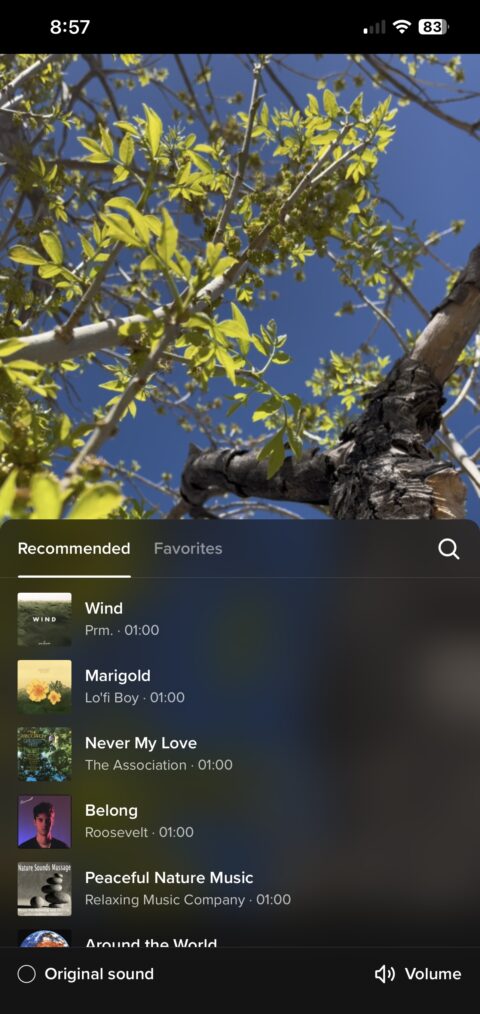
For mobile users, licensed songs can be added when creating a new post by tapping “Add Sounds” and filtering the results to licensed music.
Sounds for Businesses is rolling out now. For more, read TikTok’s announcement here.