In the wake of the one-year anniversary of the release of AMP (accelerated mobile pages), Google has released a new testing tool to help content publishers ensure their AMP pages are properly set-up and displaying correctly.
The tool is directly available at https://search.google.com/search-console/amp and can be accessed through the Google Search Console.
The testing tool is designed to work on mobile devices and uses Google’s live web-search infrastructure” to assess any AMP page using real Googlebots to provide real-time evaluations.
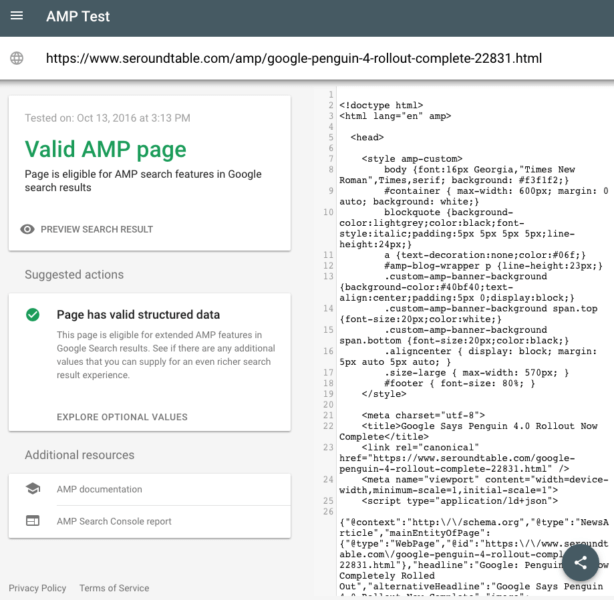
Specifically, it checks the AMP markup and structured data on the page for issues, then highlights any part of the source-code that could be creating errors. You can then click on the issues for more details about the issue.
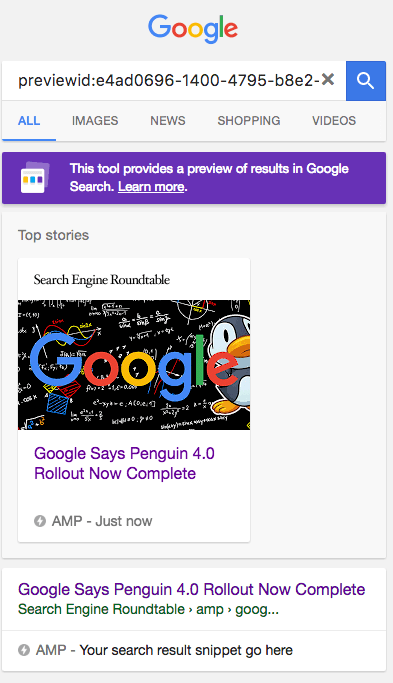
The testing tool also allows you to see a live preview of how the page may appear in Google’s search results.
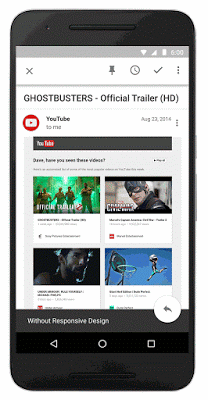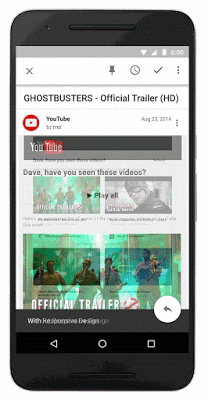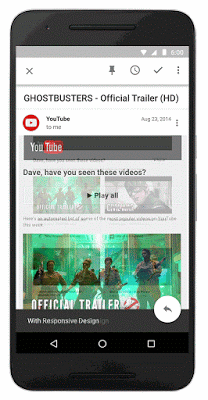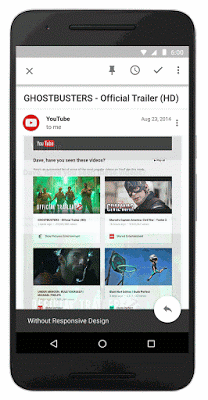
Below you can see screenshots of the tool in action, taken by Barry Schwartz: