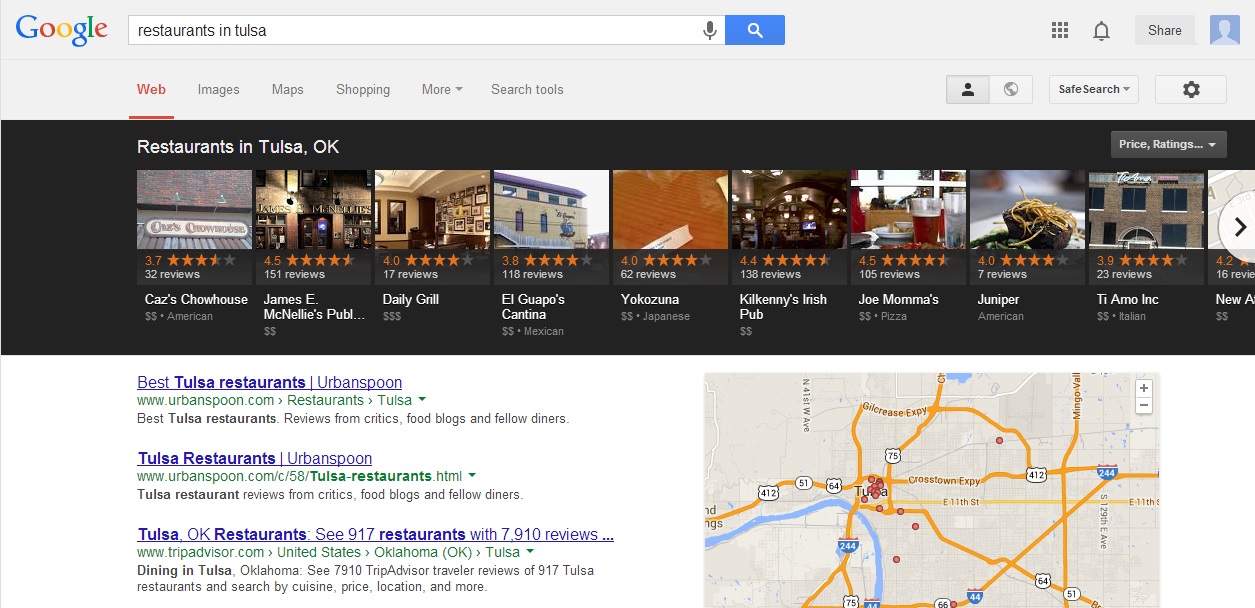
 Google’s Carousel may seem new to most searchers, but it has actually been rolling out since June. That means enough time has past for marketing and search analysts to really start digging in to see what makes the carousel tick.
Google’s Carousel may seem new to most searchers, but it has actually been rolling out since June. That means enough time has past for marketing and search analysts to really start digging in to see what makes the carousel tick.
If you’ve yet to encounter it, the carousel is a black bar filled with listings that runs along the top of the screen for specific searches, especially those that are location based or for local businesses such as hotels and restaurants. The carousel includes images, the businesses’ addresses, and aggregated review ratings all readily available at the top, in an order that seems less hierarchical than the “10 pack” listings previously used for local searches.
Up until now, we’ve only had been able to guess how these listings were decided based on surface level observations. But, this week Digital Marketing Works (DMW) published a study which finally gives us a peak under the hood and shows how businesses may be able to take some control of their place in the carousel. Amanda DiSilvestro explains the process used for the study:
- They examined more than 4,500 search results in the category of hotels in 47 US cities and made sure that each SERP featured a carousel result.
- For each of the top 10 hotels found on each search, they collected the name, rating, quantity of reviews, travel time from the hotel to the searched city, and the rank displayed in the carousel.
- They used (equally) hotel search terms—hotels in [city]; best hotels in [city]; downtown [city] hotels; cheap hotels in [city].
- This earned them nearly 42,000 data points on approximately 19,000 unique hotels.
- They looked at the correlation between a hotel’s rank in a search result based on all of the factors discussed in step 1 to determine which were the most influential.
Their report goes into detail on many of the smaller factors that play a role, but DMW’s biggest findings were on the four big factors which determine which businesses are shown in the carousel and where they are placed.
1. Google Reviews – The factor which correlated the most with the best placement in the carousel were by far Google review ratings. Both quantity and quality of reviews clearly play a big role in Google’s placement of local businesses and marketers should be sure to pay attention to reviews moving forward. However, it is unclear how Google is handling paid or fake reviews, so many might be inspired to try to rig their reviews. For long-term success, I would suggest otherwise.
2. Location, Location, Location – Seeing as how the Google Carousel seems built around local businesses, it shouldn’t be a surprise that location does matter quite a bit. Of the 1,900 hotels in the study, 50 percent were within 2 miles of the search destination, while 75 percent were within 13 minutes of travel. Businesses would benefit from urging customers to search for specific landmarks or areas of cities, as you never know exactly where Google will establish the city “center”.
3. Search Relevancy and Wording – According to the findings, Google seems to change the weight of different ranking factors depending upon the actual search. For example, searching “downtown [city] hotels” will result in listings with an emphasis on location, while “best hotels in [city]” gives results most dependent on review rankings.
4. Primary Markets and Secondary Markets – It seems both small and larger businesses are on a relatively flat playing field when it comes to the carousel. Many small hotels are able to make it into the listings, right next to huge chains. The bigger businesses may have more capabilities to solicit reviews, but no hotel is too small to be considered for the carousel.

 These changes won’t take place until November, but don’t expect a prompt roll-out. It is possible you may start seeing the changes starting the 11th, but more likely it will gradually appear over the span of a few days or even a couple of weeks.
These changes won’t take place until November, but don’t expect a prompt roll-out. It is possible you may start seeing the changes starting the 11th, but more likely it will gradually appear over the span of a few days or even a couple of weeks. It seems like everything looks different over at Google these days. Not only has their logo subtly
It seems like everything looks different over at Google these days. Not only has their logo subtly 
 Have you noticed a difference using Google on your smartphone this past week? Last week Ilya Grigorik, a Google developer advocate,
Have you noticed a difference using Google on your smartphone this past week? Last week Ilya Grigorik, a Google developer advocate,  Google AdWords announced yesterday a major reporting update to conversion tracking called Estimated Total Conversions will be rolling out over the next few weeks. The new feature provides estimates of conversions which take place over multiple devices and adds this to the conversion reporting we are already accustomed to.
Google AdWords announced yesterday a major reporting update to conversion tracking called Estimated Total Conversions will be rolling out over the next few weeks. The new feature provides estimates of conversions which take place over multiple devices and adds this to the conversion reporting we are already accustomed to. Last week SEO and online marketing professionals
Last week SEO and online marketing professionals 

