Google is warning brands that Web Stories which don’t follow through on their promised content may but cut from appearing in Google Search and Google Discover.
In an announcement, the company explained that users have expressed disinterest in Web Stories which “tease” content but require users to click through to get the full experience. As such, brands using this style of Web Story run the risk of having their content demoted.
What Are Google Web Stories?

Google’s take on the popular Story format first appeared back in 2018, going by the name of AMP Stories.
These quick, visual posts or ads function almost identically to Facebook or Instagram Stories, but appear within the Google mobile app when exploring the Discover tab or searching for websites.
One thing that makes Google’s version of these posts unique, however, is that Web Stories can easily be shared to any platform, including competing social networks.
What This Change Means For You
In the announcement, Google’s Paul Bakaus explains that “a one- or two-page teaser for your blog post doesn’t tell a satisfying story to a reader, so Google will do its very best to not show these to users.”
With this in mind, Google is planning to stop showing “teaser” based Web Stories across its platform.
If you are concerned your Web Stories may be affected, Google recommends following a few Do’s and Don’ts:
Dos:
- A shopping inspiration list that highlights products and links out to places where you can buy them.
- A short version of a recipe with complete ingredients listed that leaves more detailed instructions behind a click.
Don’ts:
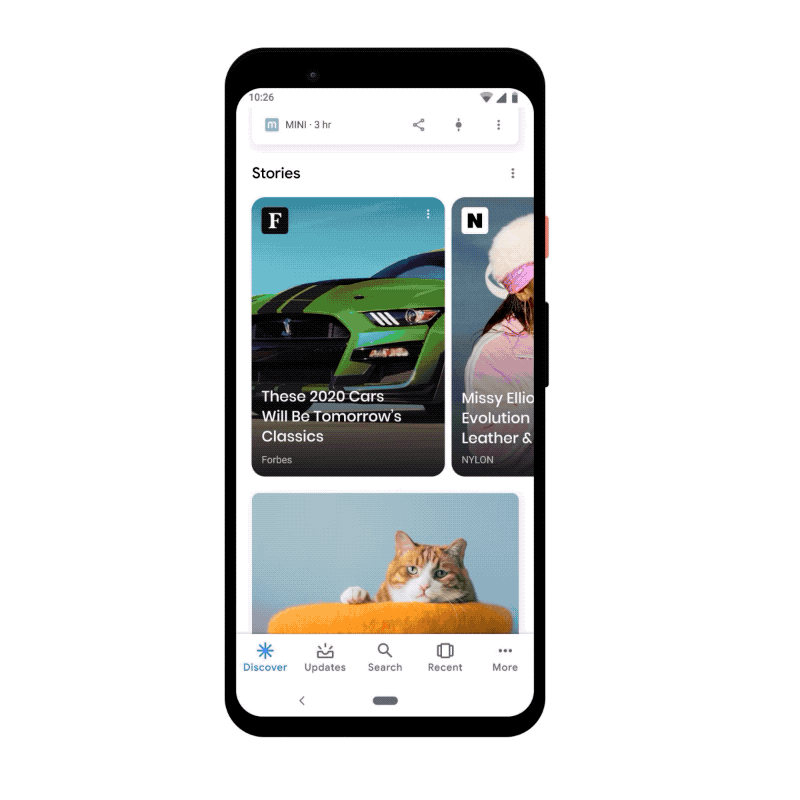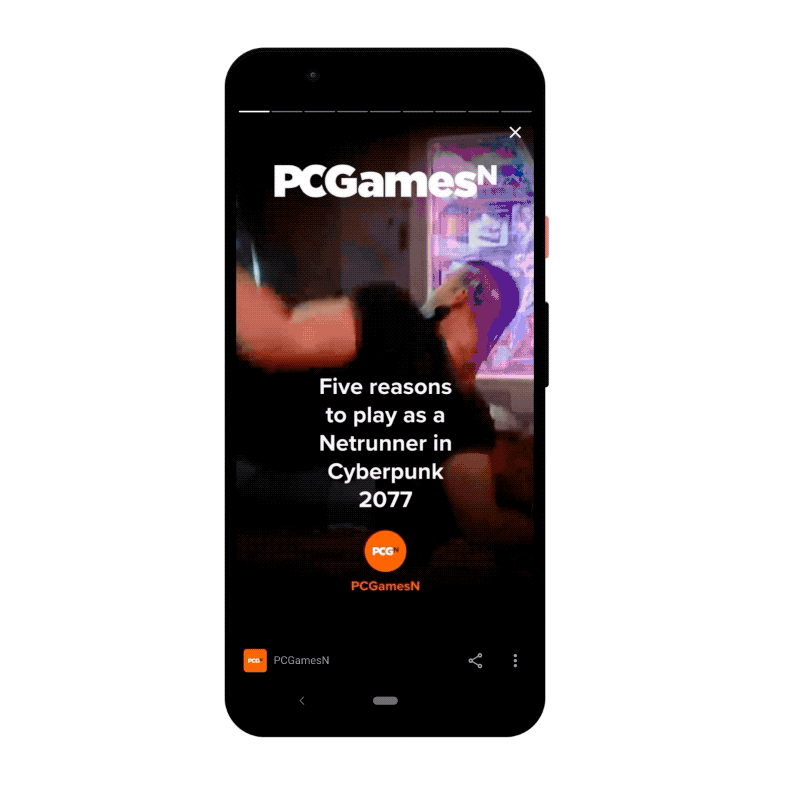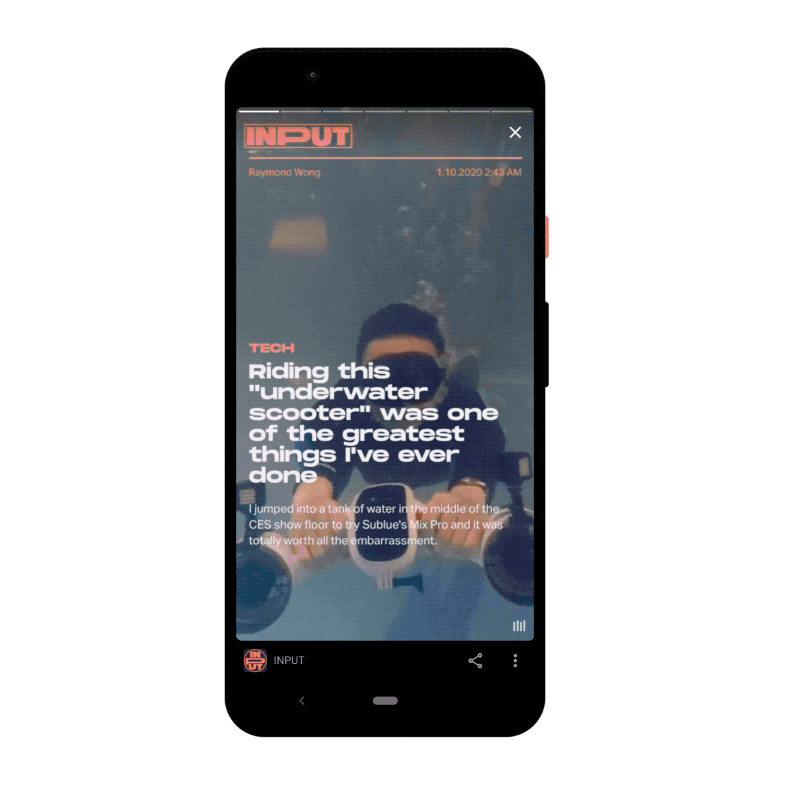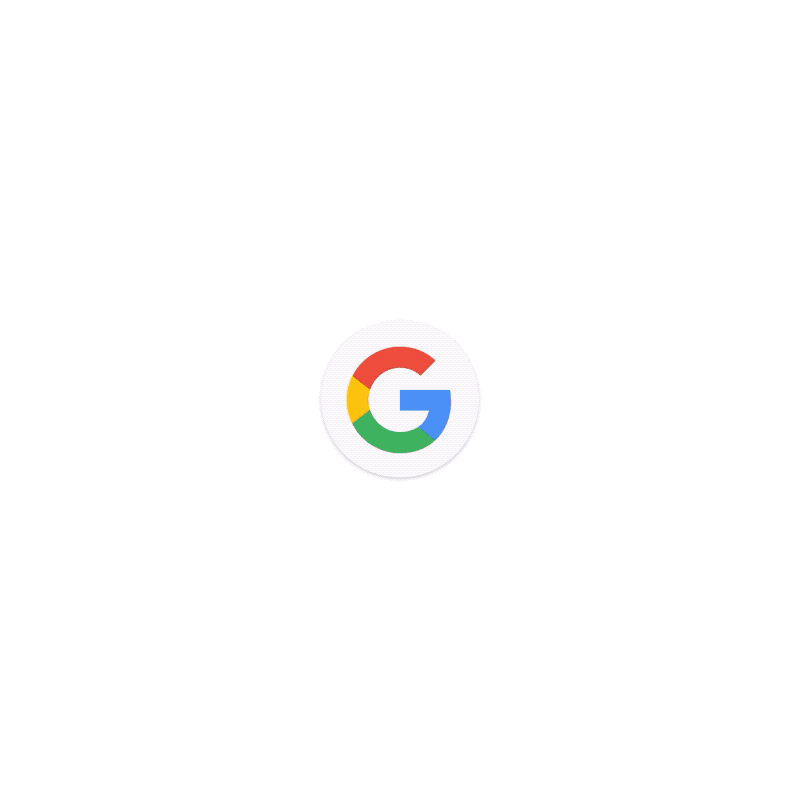
- A one-page story that mentions a recipe in the headline, but is just a bunch of photos that redirect to the website.
- A list highlighting beautiful cities in Europe, but just listing a city and a photo and pointing to the blog link for any actual information.
It is worth noting that the above example image Google shows of a recipe web story actually clearly falls into the “Don’t” category here. This highlights how unclear the actual implementation of this new policy is currently.
People are Tired of Clickbait
As Bakaus notes, users expect complete content from Stories, not a lure leading to a comprehensive blog post.
“Unfortunately, from what users are telling us, this isn’t what they want. Instead, web stories are best when they tell a full story and aren’t used to “tease” other content.
“Readers don’t like to feel forced to click through to a connected blog post to finish reading.”
How This Affects Monetization
One of the biggest reasons many brands used “teaser” Web Stories was to help drive traffic to their own monetized content. This new policy could potentially disrupt this strategy entirely.
Despite this, Google urges you to “think about the users consuming [Web Stories] and how Google showcases them.”
At the same time, the company notes that “you can directly monetize Web Stories with in-between-page ads.”
Bakaus does admit this may not be as effective or lucrative, though the company hopes to improve this situation in the future:
“A well-optimized blog post might still make you more money today, but ad networks are working on building out and expanding their Web Story integrations, so you should see both CPMs and fill rates improve over time.”
You can hear Paul’s full explanation of the policy and the best practices for creating Web Stories in his Google Web Creators video below: