Google is unveiling a new service called Fundo which helps businesses, entrepreneurs, and creatives hold and monetize video events. With Fundo, event holders can set the date for their event, sell tickets, and connect with their followers all in one space.
What Exactly is Fundo?
Fundo is an online platform which allows users to create and sell tickets to private events. Unlike many other online video event tools, there is no software or app to download. Everything is done directly on the platform’s site.
Events can be easily publicized on other platforms, using a simple link to the event page. Users can also browse for upcoming events on the site.
Who Is Fundo For?
The primary audiences for the platform appear to be businesses, consultants, and celebrities, though the tools could be used by anyone looking to have private workshops or small discussion-based events.
Specifically, the announcement calls out a few professions that may benefit from the platform:
“In addition to YouTube creators and their fans, we’re seeing authors, fitness instructors, business and lifestyle consultants and others use Fundo to find new ways to connect.”
Three Types of Events
For now, the platform allows for three different types of events to be held. These are:
1:1 Chat + Photos
The one-on-one event is pretty much what it sounds like – a way for creators to hold an event with a single individual or fan. This would typically be for a very casual conversation or low-key discussion.
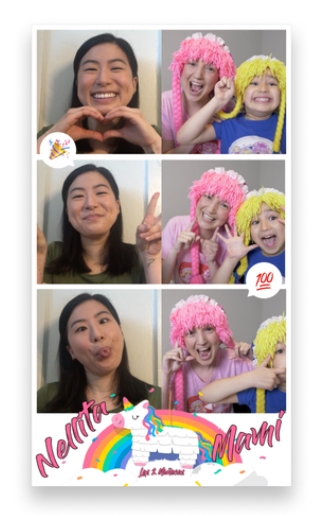
What sets this event apart is the introduction of a virtual photo booth feature which allows fans and creators to take virtual photos together.
For many professionals, this might not be all that interesting. However, YouTube celebrities or other well-known figures may find these one-on-one experiences a powerful way to connect with fans and still be able to monetize the experience.
Meet and Greets
Meet and Greets are largely similar to the 1:1 type events, only with several fans or followers at a time.
In the announcement, Google focuses on using these events to connect YouTube creators with fans for small roundtables and hangouts.
As the company describes it:
“As a fan, you’ll have a variety of experiences to choose from. Join the Q&A with… channel members in a group Meet & Greet…”
Workshops
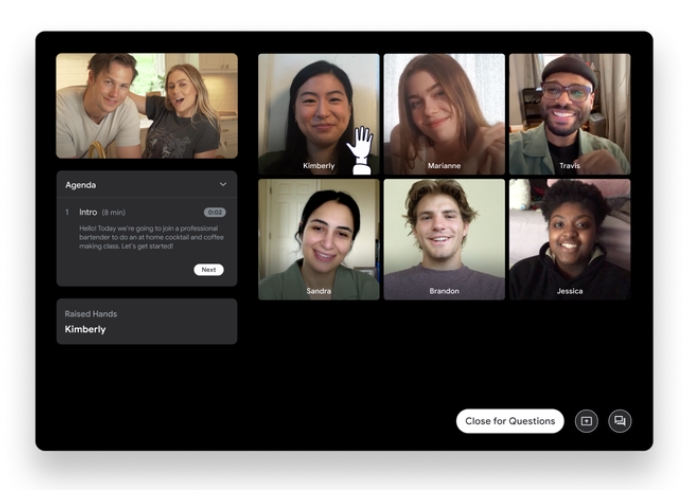
For most, this is going to be where Fundo really shines.
Workshops allow for consultants, experts, and leaders to hold special events where they guide attendants through a process.
For example, salon workers struggling to bring in clients during the pandemic can use Fundo to hold classes teaching basic hair care or styling to bring in revenue on the side.
At the same time, these events help promote your core business by showing your abilities and expertise to all who attend.
No matter what field you are in, Fundo workshops offer an opportunity to build your brand, showcase your goods, and connect with existing customers or fans all at once – and bring in a little bit of revenue while you’re doing it.
How Secure Are Fundo Events
After the rise of Zoom Bombing – the act of breaking in and disrupting Zoom events – one of the biggest concerns for many virtual event holders is privacy and security.
While the company doesn’t go into detail on how it prevents this from occurring, Google says there are no ways for users to crash an event without a ticket.
As the announcement says:
“Safety is a top priority. Because Fundo is checking everyone’s ticket, there’s no risk of uninvited guests. We also have reporting and flagging features to curtail abuse.”
To sign up or find out more, check out the links below:
Sign Up: https://fundo.town/creators
Google’s Announcement: https://blog.google/technology/area-120/fundo/
Help Document: https://intercom.help/fundo/en/articles/4169996-how-does-fundo-work