Just How Much of the Market Does Google Actually Control? Making Sense of Conflicting Reports
Every month, comScore releases a “U.S. Search Engine Rankings” report illustrating the market shares of the most commonly used search engines. From month to month the results have stayed largely the same for over a year, with Google taking in almost exactly two-thirds of the market and the other search engines like Bing and Yahoo slowly growing and shrinking by minuscule percentages.
ComScore’s report is widely trusted by most of the online marketing community, but recently analysts from Conductor attempted to challenge comScore’s findings with their own report claiming Google actually rakes in a significantly larger percentage of searches. They even went as far as to title their reports “Why You Shouldn’t Trust comScore’s Numbers for Search Engine Market Share.”
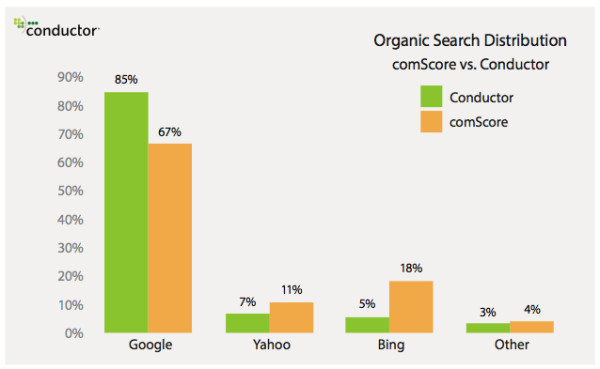
For such an obvious attack on another analytics firm, you would assume Conductor was publishing new information or even comparing the same factors. As Danny Sullivan from Search Engine Land shows in his article reviewing Conductor’s findings however, Conductor’s findings shouldn’t be news to anyone paying attention, and they don’t disprove comScore’s findings.
The issue i that, when people hear that Google controls two-thirds of the search market many publishers assume they should see close to the same proportion of traffic coming from the search engine. Instead, most publishers see significantly more traffic from Google than their market score seemingly indicates.But, market share isn’t a measurement of the traffic sites receive.
The monthly report from comScore reflects the number of actual searches conducted from the major search engines. Most importantly, their report isn’t affected by where the user goes after clicking on a search listing. Sullivan refers to this type of measurement as “before-the-click” behavior. Every search gets counted equally, no matter what the destination is.
Conductor’s analysis instead focuses on “post-click” behavior, or the traffic publishers receive from search engines. In their report, the information that matters most is the post-click activity. If someone does a search and clicks on a link that leads them back into the search engine, it isn’t measured in Conductor’s report.
The discrepancy between these two types of reports isn’t anything new. In fact, Sullivan cites 2006 as the last time it received significant attention due to Rich Skrenta writing that Google’s “true market share” being 70% while most measurement services were estimating their market share at 40%. Most entertainingly, Sullivan’s response then still perfectly explains why a gap might form. So much changes in search on a daily basis it is always noteworthy when something manages to be admirably accurate after eight years. As Danny Sullivan wrote at the time:
“But a search for something on Yahoo Sports? That might be counted as a “search” and it is – but it’s not the type of search that would register with site-based metrics. The searcher might stay entirely inside Yahoo.”
Search engines with the largest gaps favor their own services more than others, which would suggest that Bing’s 13% gap indicates they direct searchers to their own services and platforms more than any other search engine. Surprisingly, Google appears to favor themselves the least, with a -18% gap.
Of course, there is always the possibility that this gap could be created or exacerbated by other factors that may not have been in play at the time. When Sullivan asked comScore for its opinion on the difference between its reports and Conductor’s recent study he was told mobile search could also potentially be an influence. Google has a higher share of mobile search than compared to desktop figures, and comScore’s reports only include data from desktop users.
Both reports serve their own purposes, but both also highlight the same issue. Google has a huge hold on search traffic that should be recognized and planned for. But, those who buy into Conductor’s study may be tempted to ignore the other search engines entirely. To each their own, but my opinion still favors an approach which puts the most weight in Google but doesn’t cut out the other search engines too much.






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!