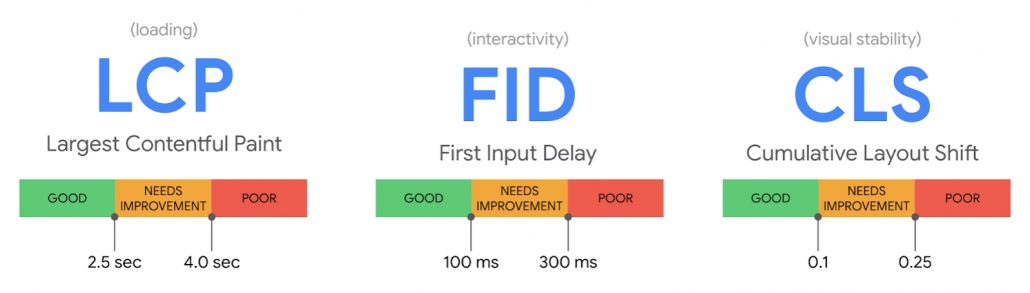
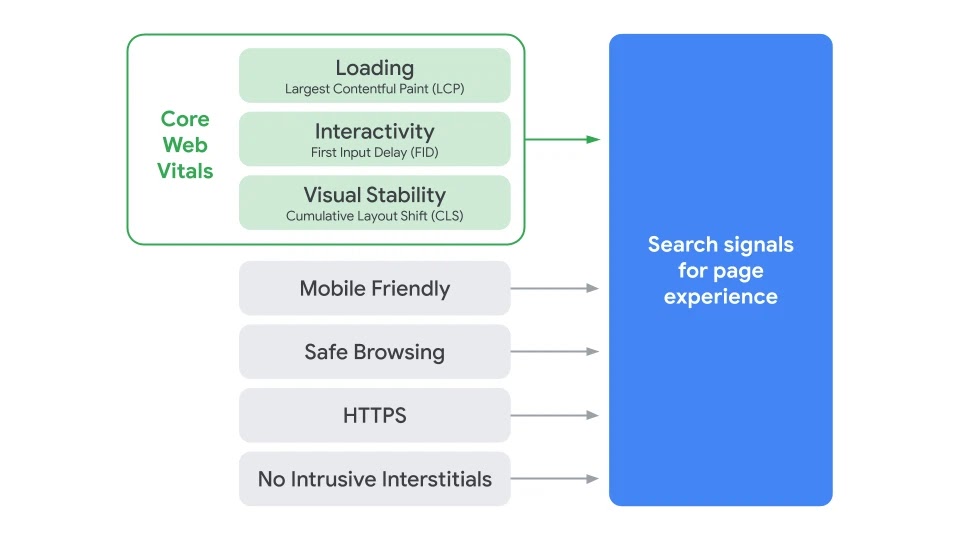
Google confirmed this week that its most recent broad core update, which began rolling out on December 3, 2020, is now completely rolled out to all search users.
Google’s SearchLiason account announced “the December 2020 Core Update rollout is complete,” yesterday following almost two weeks of anxious waiting from webmasters and SEOs.
What We Know
Google is notoriously tight-lipped about its “secret recipe” used to rank websites around the world. Still, this update was big enough that the search engine felt it necessary to alert the public when the December core update started rolling out.
This may simply be because the update rollout is global, affecting all users in all countries, across all languages, and across all website categories.
However, early signs suggest the algorithm update was uncommonly big, with many reporting huge gains or losses in organic traffic from search engines.
What Is a Broad Core Update?
Google’s “broad core updates” are essentially a tuneup of the search engine’s systems. Rather than adding a specific feature, targeting a singular widespread issue like linkspam, or prioritizing a ranking signal, a core update more subtly tweaks Google’s existing systems. This can be rebalancing the impact of some search signals, refining Google’s indexing tools, or any other combination of changes.
What To Do If You Are Affected
The first thing any webmaster should do is thoroughly check their analytics to ensure they haven’t experienced a significant change in search traffic.
If you have, you will be disappointed to hear that Google has not provided any specific guidance for how to recover from this update. In fact, the company suggests a negative impact from a core update may not even reflect any actual problems with your website.
What the search engine does offer is a series of questions to consider if you have been affected by a recent core update. Though not as useful as actual suggestions for fixing lost rankings, these questions can help you assess your site and identify areas for improvement before the next broad core update.