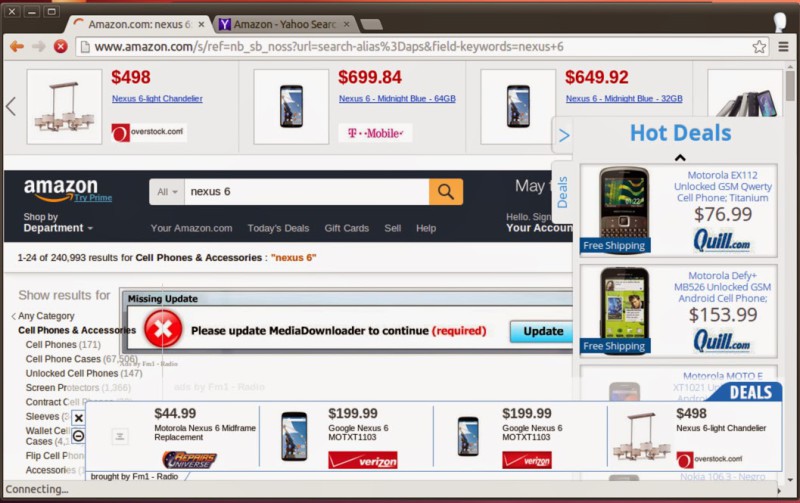
Examples of injected ads ‘in the wild’
A new study from Google and the University of California, Berkeley and Santa Barbara has found that over 3,000 advertisers have been the victims of ad injection software, including major brands such as Sears, Walmart, Target, and eBay.
Ad injectors have long been a boon for webmasters, as the troublesome and occasionally malicious programs insert unwanted ads into web pages costing publishers in ad revenue and causing advertisers to pay for traffic from ads they never intended to buy.
The study exposes a network of companies that profit from and facilitate these unwanted ads and to show just how widespread the issue is. Google says it has received more than 100,000 complaints from users about ad injectors since just the start of this year.
Ginny Marvin from Marketing Land thoroughly breaks down how ad injection works:
The ad injectors comes in the form of browser extensions and software applications that infect a user’s browser. Google found more than 50,000 browser extensions and 34,000 software applications that had hijacked user’s browsers to inject ads. In nearly 30 percent cases, the software bundles were “outright malicious”, not only injecting ads but stealing account credentials, hijacking users’ search queries and reporting user activity to third parties for tracking purposes.
Google found the ad injector software being distributed onto users computers by 1,000 affiliate businesses, including known adware browser extensions, Crossrider, Shopper Pro and Netcrawl. These companies aim to spread as many ad injector software downloads as possible in a number of ways, including bundling their applications with popular downloads (who hasn’t fallen victim to the pre-checked box for an add-on during a software download?), blatant malware distribution and extensive social media campaigns. They then collect affiliate fees when users click on injected ads.
The ad injectors get the ads from about 25 ad injection library companies such as Superfish and Jollywallet, which in turn source and target ads from relationships with a handful of ad networks and shopping programs. It’s these libraries that pass on a fraction of the profits to the affiliates.
Google found that 77 percent of all injected ads originated from just one of these three ad networks: Dealtime.com, Pricegrabber.com and Bizrate.com.
This network is massive for even the most sophisticated spam and shady marketing systems. Google used a custom-built ad injection detector on Google sites and found that 5.5 percent of unique IP addresses (representing millions of users) accessed Google sites that had some form of injected ads.
Don’t think your Mac is safe either. Google also saw that 3.4 percent of page views on Apple machines and 5.1 percent on Windows machines showed clear signs of ad injection software.
To combat the problem, Google says it has taken down 192 deceptive Chrome browser extensions from the Chrome Web Store and instituted new user protections to prevent similar extensions from making it into the store in the future.
The full report will be presented later this month at the IEEE Symposium on Security & Privacy, but you can read Google’s announcement of the study results here.



